What are compile & link options in Custom directives?
Understanding the compile vs. link option is one of the more advanced topics across Angular, and it gives us a feel how actually Angular works. Out of both the functions,link function is used very often. Basically, both are mutually exclusive, i.e., if both the options are set, then compile will overwrite the link functions defined. The concept of compile and link
comes from C language, where you first compile the code and then link
it to actually execute it. The process is very much similar in AngularJS
as well.Compile: It traverses the DOM and collects all of the directives and deals with transforming the template DOM. The result is a linking function.
Link: The link function deals with linking scope to the DOM.
Using Code for Compile
While defining a custom directive, we have the option to define a link against which either we can define a function or we have the option to assign an object which will have pre & post functions.If compile is defined as defined below, then it will override the
link function as shown in the below example: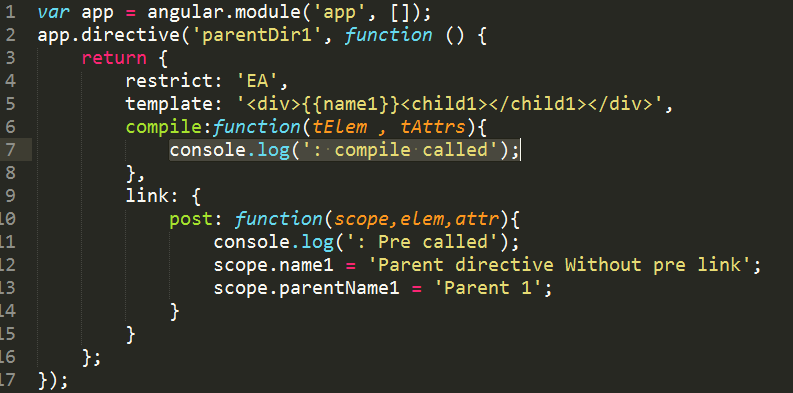
Using Code for Pre & Post Link
While defining a custom directive, we have the option called “link”
against which either we can define a single function or we have the
option to assign an object in which we can define further two functions,
i.e., Pre-link and Post-link functions.If only a single function is defined against
link option, that will be the same as Post link function.Both Pre & Post link functions have the same syntax as defined below but the only difference is the order in which they get executed.
Link Example
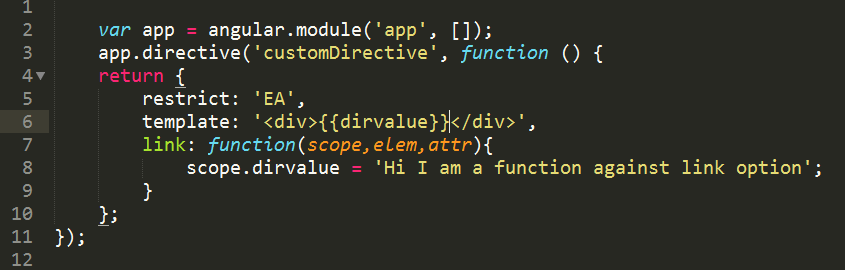
In the above example, we are defining a function against
link option which will get executed before linking scope and the template.Pre & Post Functions Examples
Defining only Post
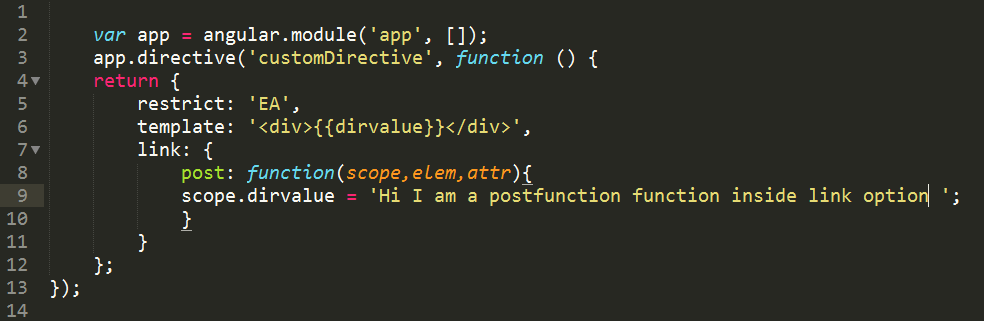
Defining post is the same as the link option defined with a normal function as defined in above link example.
Defining Pre & Post
The signature of the pre-link function is the same as that of a post-link. The only difference between the pre-link and a post-link is the order in which they get executed.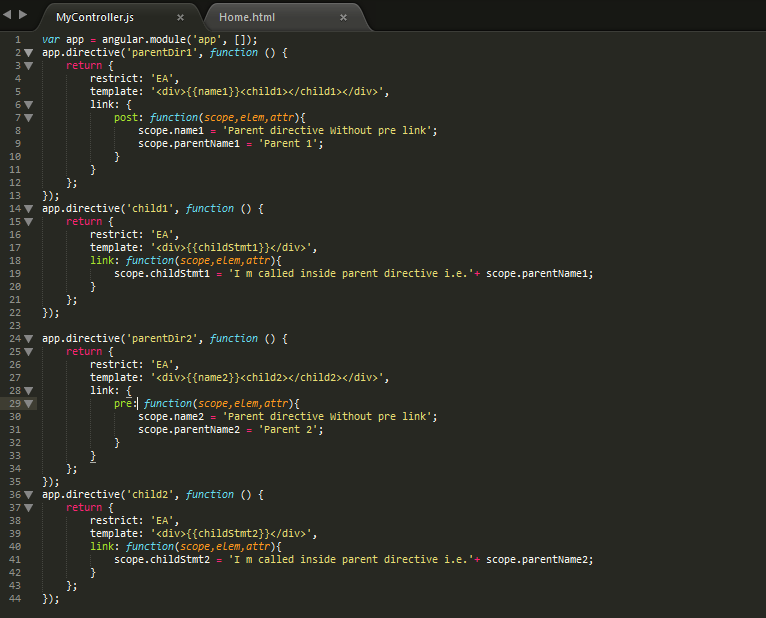
In the above example, there is a directive defined with name
parentDir1 which has a child directive called child1 and
both are defined using post / link functions due to which the output
shows that scope of parent is unable to be accessed in child scope due
to which name of parent is printed as undefined.And to this problem, the solution is Pre-link function which is shown in the above example with
parentDir2 which is having child directive called child2 and parent is defined with pre-link function and child is defined with post link function.Below is the output of the above example:
